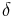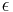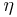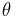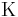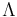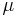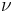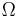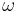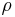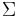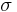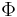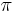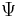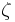List of common physics notations
Contents |
Latin characters
| Symbol | Meaning | SI Unit of Measure |
|---|---|---|
 |
area | |
| magnetic vector potential | ||
| Amplitude | ||
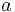 |
acceleration | meter per second squared (m/s²) or (ms−2) |
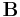 |
magnetic flux density also called the magnetic field density or magnetic induction |
tesla (T), or equivalently, weber per square meter (Wb/m²) |
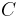 |
capacitance | |
| heat capacity | ||
| constant of integration | varied depending on context | |
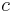 |
speed of light (in a vacuum) | Meters per Second (m/s) |
| speed of sound | Meters per Second (m/s) | |
| specific heat capacity | ||
| viscous damping coefficient | kilograms per second | |
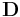 |
electric displacement field also called the electric flux density |
coulomb per square meter (C/m²) |
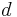 |
distance | meter (m) |
| impact parameter | meter (m) | |
| diameter | ||
differential (e.g. 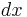 ) ) |
||
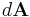 |
differential vector element of surface area A, with infinitesimally small magnitude and direction normal to surface S |
square meter (m²) |
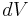 |
differential element of volume V enclosed by surface S | cubic meter (m³) |
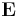 |
electric field | volt per meter (V/m) |
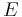 |
energy | joule (J) |
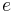 |
eccentricity | unitless |
| 2.71828... (base of the natural logarithm), electron, elementary charge | ||
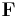 |
force | newton (N) |
 |
frequency | hertz (Hz) |
| function | ||
| friction | ||
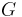 |
the gravitational constant | newton meter squared per kilogram squared (N m²/kg²) |
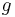 |
acceleration due to gravity | |
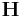 |
magnetic field strength also called just magnetic field |
ampere per meter (A/m) |
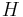 |
Hamiltonian | joule (J) |
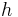 |
height | |
| Planck's constant | joule second (J s) | |
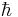 |
reduced Planck's constant 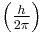 |
joule second (J s) |
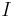 |
action | joule second (J s) |
| intensity | watt per square meter (W/m²) | |
| sound intensity | watt per square meter (W/m²) | |
| electric current | ampere (A) | |
| moment of inertia | ||
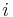 |
Cartesian x-axis basis unit vector | unitless |
| intensity | watt per square meter (W/m²) | |
| imaginary unit | ||
 |
free current density, not including polarization or magnetization currents bound in a material |
ampere per square meter (A/m²) |
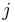 |
Cartesian y-axis basis unit vector | unitless |
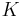 |
kinetic energy | joule (J) |
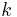 |
Cartesian z-axis basis unit vector | unitless |
| Boltzmann constant | joule per kelvin (J/K) | |
| wavenumber | ||
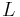 |
inductance | henry (H) |
| luminosity | watt (W) | |
| angular momentum | newton metre seconds (N·m·s or kg·m2s−1) | |
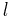 |
length | |
 |
magnetization | ampere per meter (A/m) |
| moment of force often simply called moment or torque |
newton meter (N m) | |
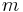 |
mass | kilogram (kg) |
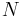 |
normal vector | unit varies depending on context |
| atomic number | unitless | |
 |
refractive index | unitless |
| principal quantum number | unitless | |
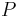 |
power | watt (W) |
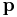 |
momentum | kilogram meter per second (kg m/s) |
| pressure | pascal (Pa) | |
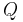 |
Electric Charge | coulomb (C) |
| Heat | joule (J) | |
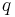 |
electric charge | coulomb (C) |
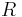 |
Electrical resistance | ohm (Ω) |
| Ricci tensor | unitless | |
| radiancy | ||
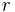 |
radius of rotation or distance between two things such as the masses in Newton's law of universal gravitation | meter (m) |
| radius vector (position) | ||
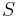 |
surface area | m2 |
| entropy | J/K | |
| action | ||
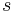 |
arc length | meter (m) |
| displacement | ||
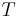 |
period | second (s) |
| Thermodynamic Temperature also called absolute temperature |
kelvin (K) | |
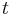 |
time | second (s) |
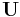 |
four-velocity | meter per second (m/s) |
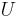 |
potential energy | joule (J) |
| internal energy | joule (J) | |
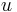 |
relativistic mass | kilogram (kg) |
| energy density | joule per cubic meter (J/m³) or joule per kilogram (J/kg) depending on the context | |
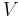 |
voltage also called electric potential difference |
volt (V) |
| volume | m3 | |
| shear force | ||
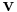 |
velocity | meter per second (m/s) |
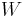 |
mechanical work | |
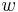 |
width | m |
 |
a generic unknown | varied depending on context |
| displacement | ||
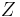 |
Electrical impedance |
Greek characters
Other characters
| Symbol | Name | Meaning | SI Unit of Measure |
|---|---|---|---|
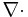 |
nabla dot | the divergence operator often pronounced "del dot" |
per meter (m−1) |
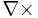 |
nabla cross | the curl operator often pronounced "del cross" |
per meter (m−1) |
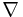 |
nabla | del (differential operator) | |
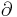 |
"der", "dow", "die", "partial" or simply "d" | partial derivative (e.g. 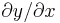 ) ) |
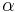
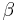
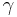

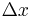 )
)